Tesla's Transformer Division Stumbles: Mass Exodus of Top Talent Signals Rocky Start
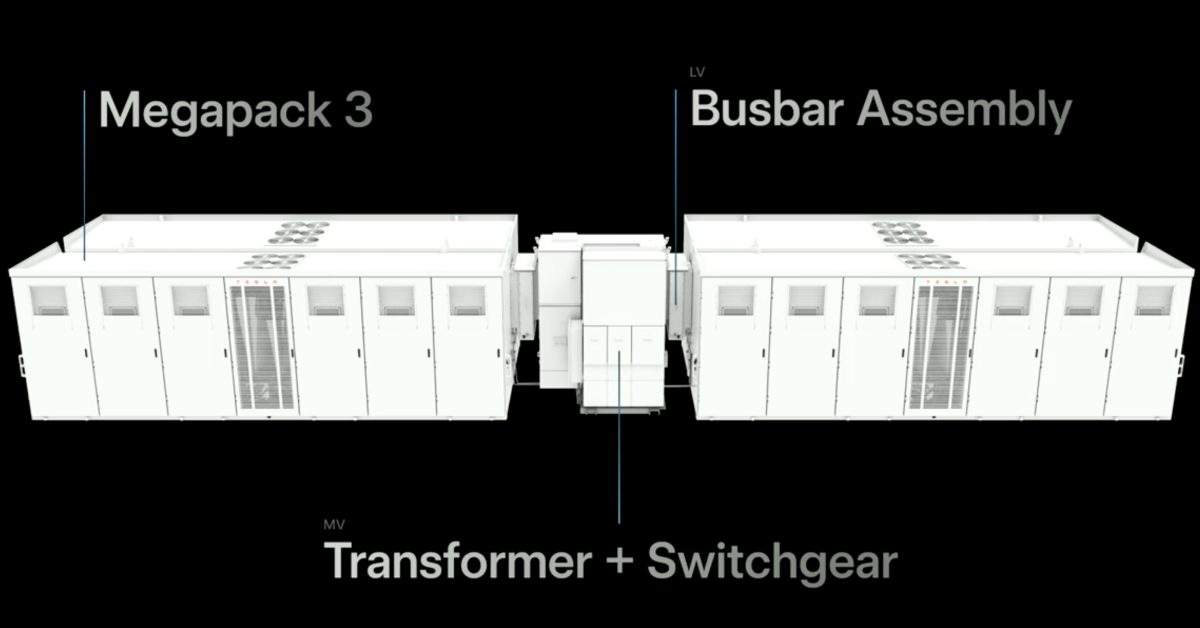
Tesla is venturing into uncharted territory by announcing its plans to manufacture electrical transformers, marking a bold expansion beyond its core electric vehicle and clean energy businesses. The innovative move signals the company's growing ambition to disrupt yet another critical infrastructure sector.
This strategic decision comes as Tesla continues to seek vertical integration and reduce dependency on external suppliers. By producing its own electrical transformers, the company aims to potentially lower costs, improve supply chain resilience, and leverage its expertise in electrical engineering and power management.
While details about the production timeline and scale remain limited, the announcement underscores Tesla's ongoing commitment to pushing technological boundaries and creating comprehensive energy solutions. The move could potentially revolutionize how electrical transformers are designed, manufactured, and deployed in both industrial and residential settings.
Industry experts are closely watching this development, recognizing that Tesla's entry into transformer production could bring innovative design approaches and advanced technological capabilities to a traditionally conservative sector.








