Mosquito Menace: West Nile Virus Surges Beyond Typical Levels, Health Officials Sound Alarm
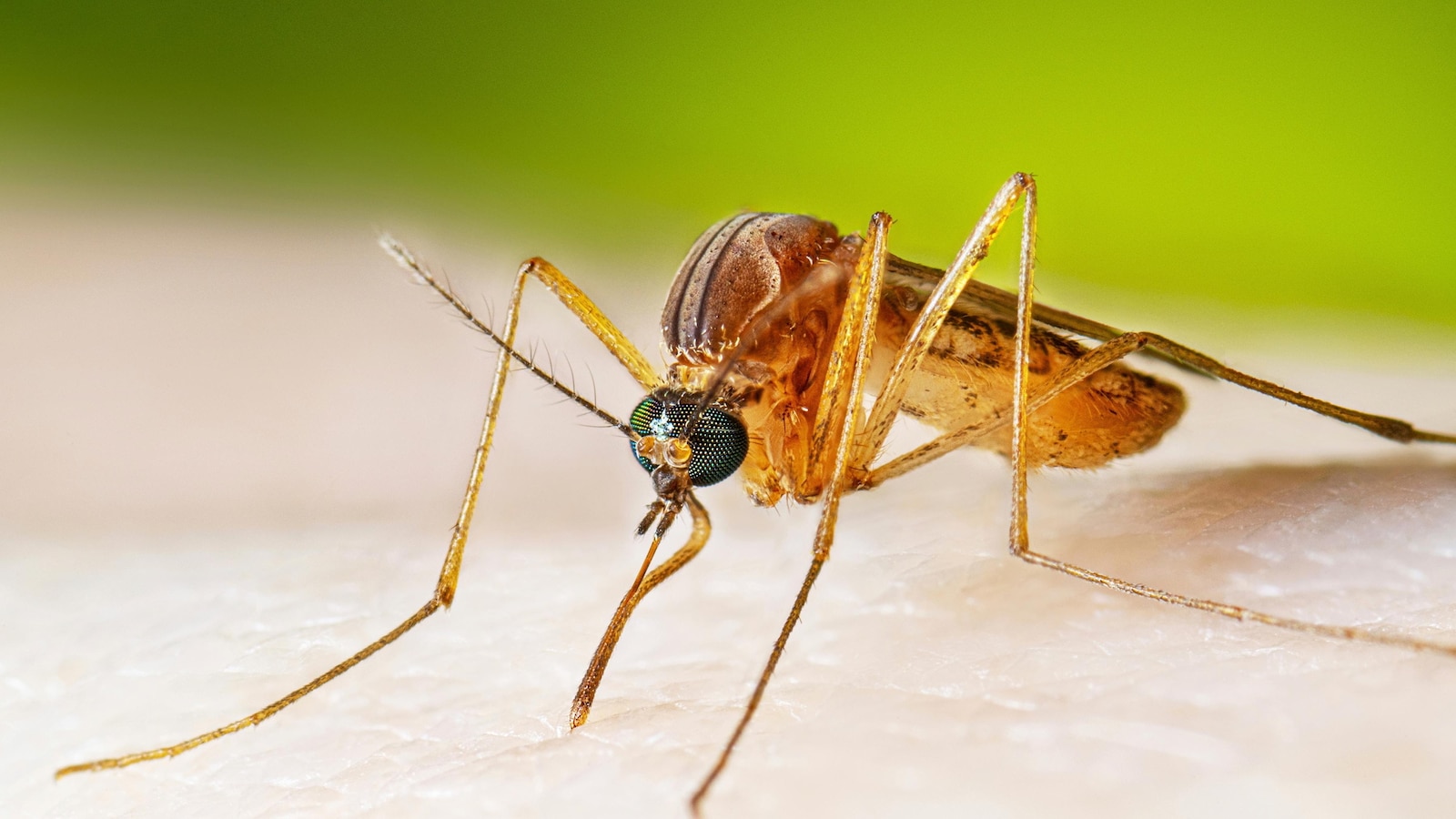

Health authorities are sounding the alarm this season as West Nile virus infections surge dramatically, with cases climbing a staggering 40% above typical annual levels. The unexpected spike has prompted increased vigilance and public health warnings across affected regions.
Experts suggest the rise in infections may be linked to warmer temperatures and increased mosquito populations, creating ideal conditions for virus transmission. Residents in high-risk areas are being advised to take extra precautions, such as using insect repellent, wearing long sleeves, and eliminating standing water where mosquitoes breed.
While most West Nile virus infections remain mild, health officials emphasize the importance of monitoring symptoms and seeking medical attention if more serious signs develop. The dramatic increase in cases serves as a critical reminder of the ongoing public health challenges posed by mosquito-borne diseases.