Canine Crisis: Bangkok Trembles as Rabid Strays Threaten Urban Health
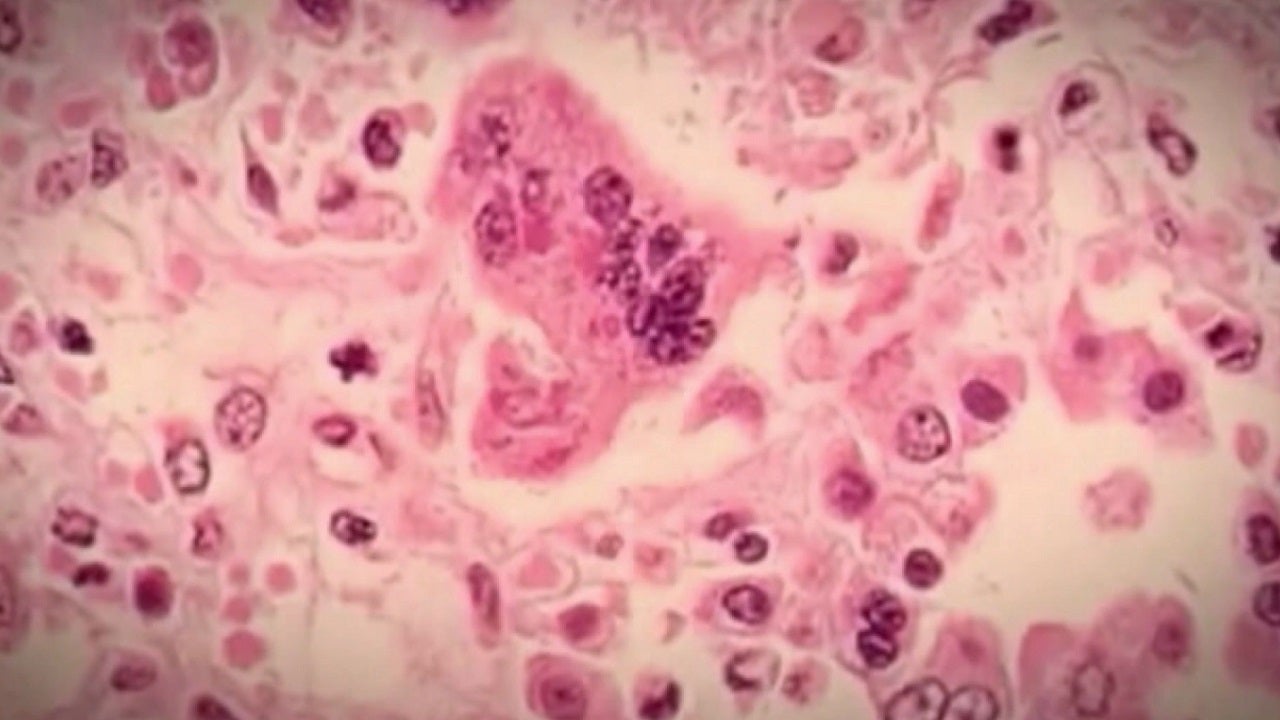
Bangkok is on high alert as health officials scramble to contain a potential rabies outbreak following the discovery of infected stray dogs in several city districts. Local authorities have implemented urgent measures to protect residents and control the spread of this dangerous viral disease.
The detection of rabies-positive stray dogs has prompted immediate public health interventions, with city officials warning citizens to exercise extreme caution when encountering street animals. Residents are advised to avoid contact with stray dogs and report any suspicious animal behavior to local health departments.
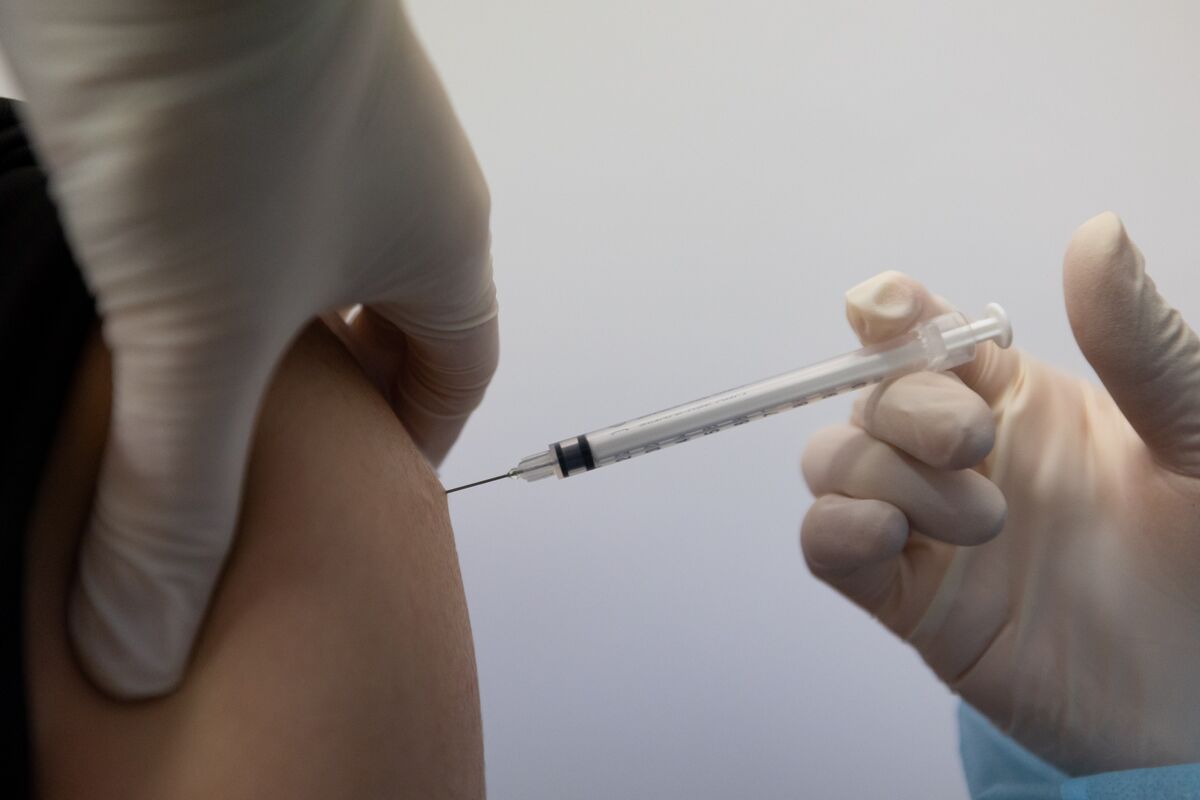
Public health teams are now conducting comprehensive vaccination and animal control campaigns to minimize the risk of transmission. These efforts include capturing and testing stray dogs, implementing widespread vaccination programs, and educating the public about rabies prevention and safety protocols.
The alert serves as a critical reminder of the ongoing challenges posed by stray animal populations in urban environments and the importance of proactive disease management strategies. Citizens are urged to remain vigilant and cooperate with local health authorities to prevent potential rabies transmission.