Groundwater Crisis: San Pedro River's Lifeline Vanishes as Military and Urban Demands Drain Hope
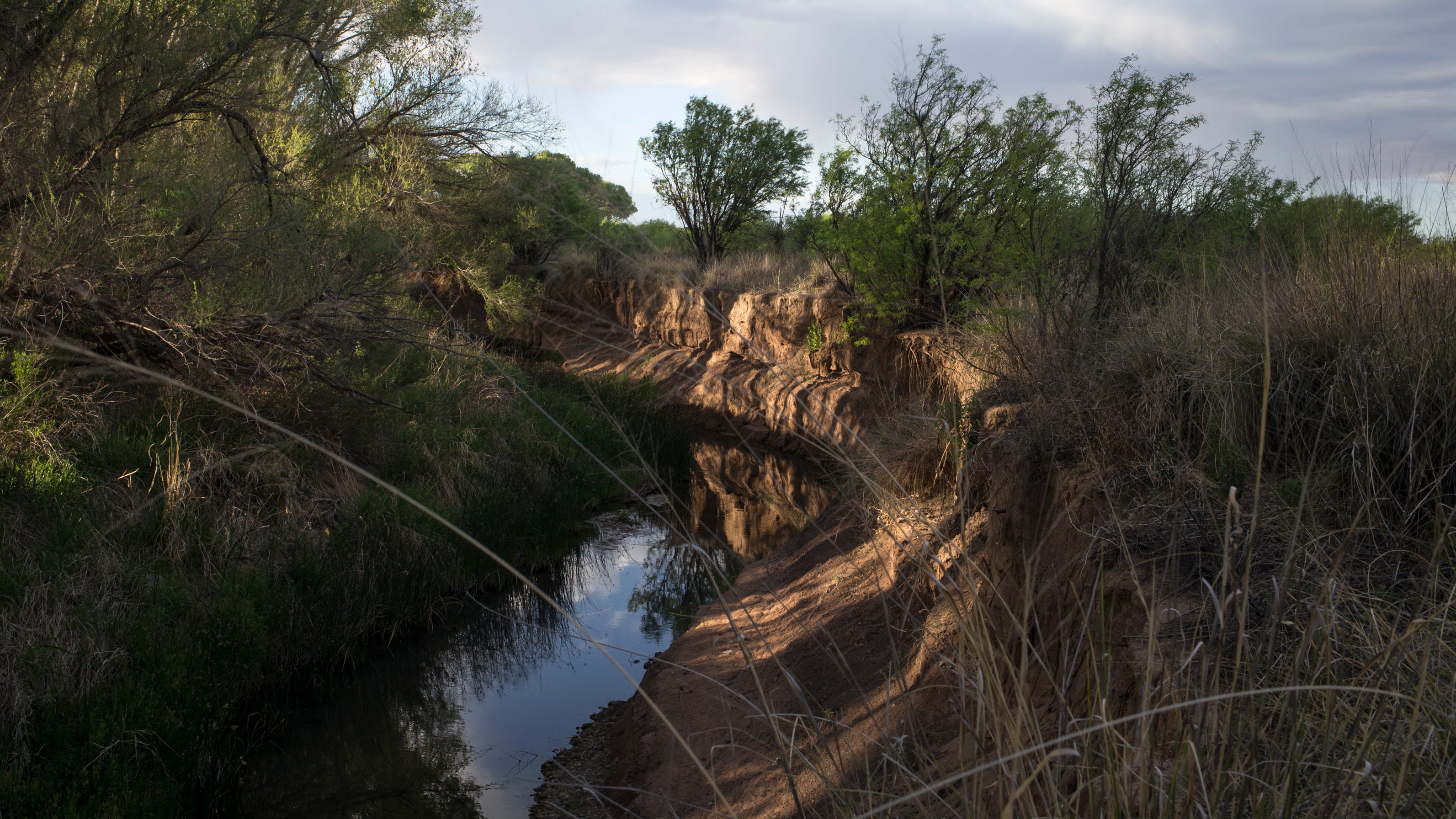

In a stark warning of environmental stress, a long-monitored well along the San Pedro River has succumbed to unprecedented drought, running completely dry for the first time in nearly four decades. This critical water level collapse serves as a powerful indicator of the region's rapidly diminishing groundwater resources, highlighting the growing challenges faced by this vital ecological corridor.
The dried-up well represents more than just a statistical anomaly; it is a tangible symbol of the increasing water scarcity threatening the delicate ecosystem of the San Pedro River. Hydrologists and environmental experts view this event as a significant milestone that underscores the urgent need for comprehensive water conservation strategies and climate adaptation measures.
Local researchers are now closely monitoring the situation, recognizing that this watershed moment could signal broader environmental changes impacting the river's complex and fragile ecosystem. The dramatic drop in the water table not only threatens local wildlife but also raises serious concerns about the long-term sustainability of water resources in the region.