AI Breakthrough: Smart Algorithms Craft Eco-Friendly Plastics That Could Save Our Planet
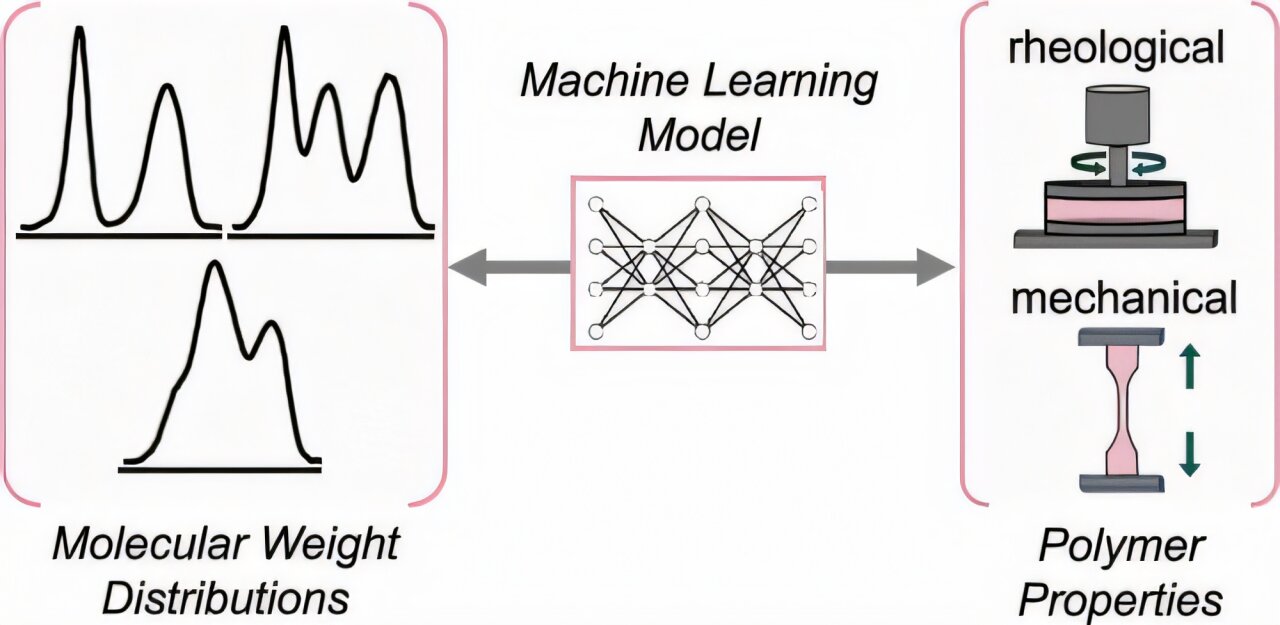
In the vast world of modern manufacturing, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) stands as a titan of industrial production. Every year, a staggering 100 million metric tons of this versatile plastic are created, consuming an almost unimaginable amount of energy—more than 15 times the annual power requirements of New York City.
This ubiquitous material, found in everything from milk jugs and shampoo bottles to cutting-edge industrial applications, represents a remarkable testament to human engineering. Yet, its production comes with a significant environmental footprint that often goes unnoticed by consumers.
The sheer scale of HDPE manufacturing is both impressive and sobering. Each ton produced requires an enormous energy investment, highlighting the complex relationship between industrial innovation and environmental sustainability. As global demand for plastics continues to rise, the challenge becomes finding more energy-efficient and eco-friendly production methods that can meet the world's growing needs without compromising our planet's delicate ecological balance.
Researchers and manufacturers are increasingly focused on developing greener alternatives and more sustainable production techniques, recognizing that the future of plastic production must be as much about conservation as it is about creation.
