Climate Shift Unveils Hidden Marine Boom: Greenland's Icy Transformation Sparks Ecosystem Revival
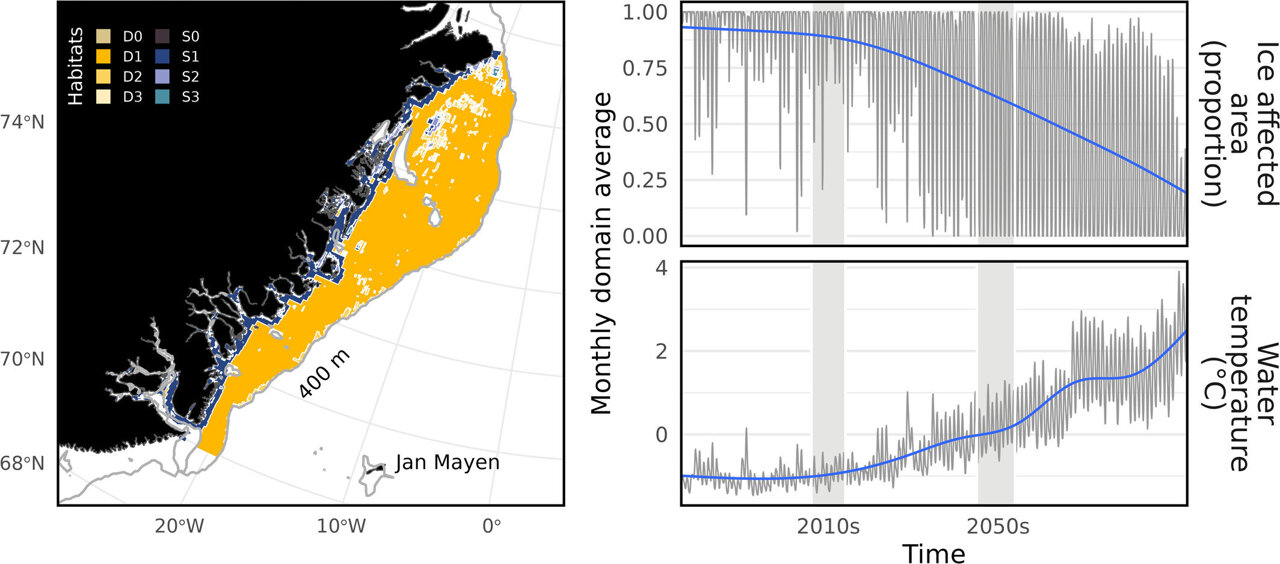
A groundbreaking study reveals exciting potential for marine biodiversity in the pristine waters off north-east Greenland. Researchers predict a remarkable expansion of marine life by over 25%, signaling a significant ecological transformation in this remote Arctic region.
The study highlights the dynamic nature of marine ecosystems in one of the world's most challenging environments. As climate patterns shift and ocean conditions evolve, the north-east Greenland coastline could become a thriving hub of marine biodiversity, offering scientists a fascinating glimpse into the adaptive capabilities of Arctic marine life.
This promising research not only underscores the resilience of marine ecosystems but also provides crucial insights into the potential long-term impacts of environmental changes in polar regions. Marine biologists and climate researchers are particularly excited about the implications of this projected expansion, which could have far-reaching consequences for understanding Arctic marine biodiversity.
