Silent Threat: Why 4 in 10 Diabetes Patients May Be Gambling with Their Health
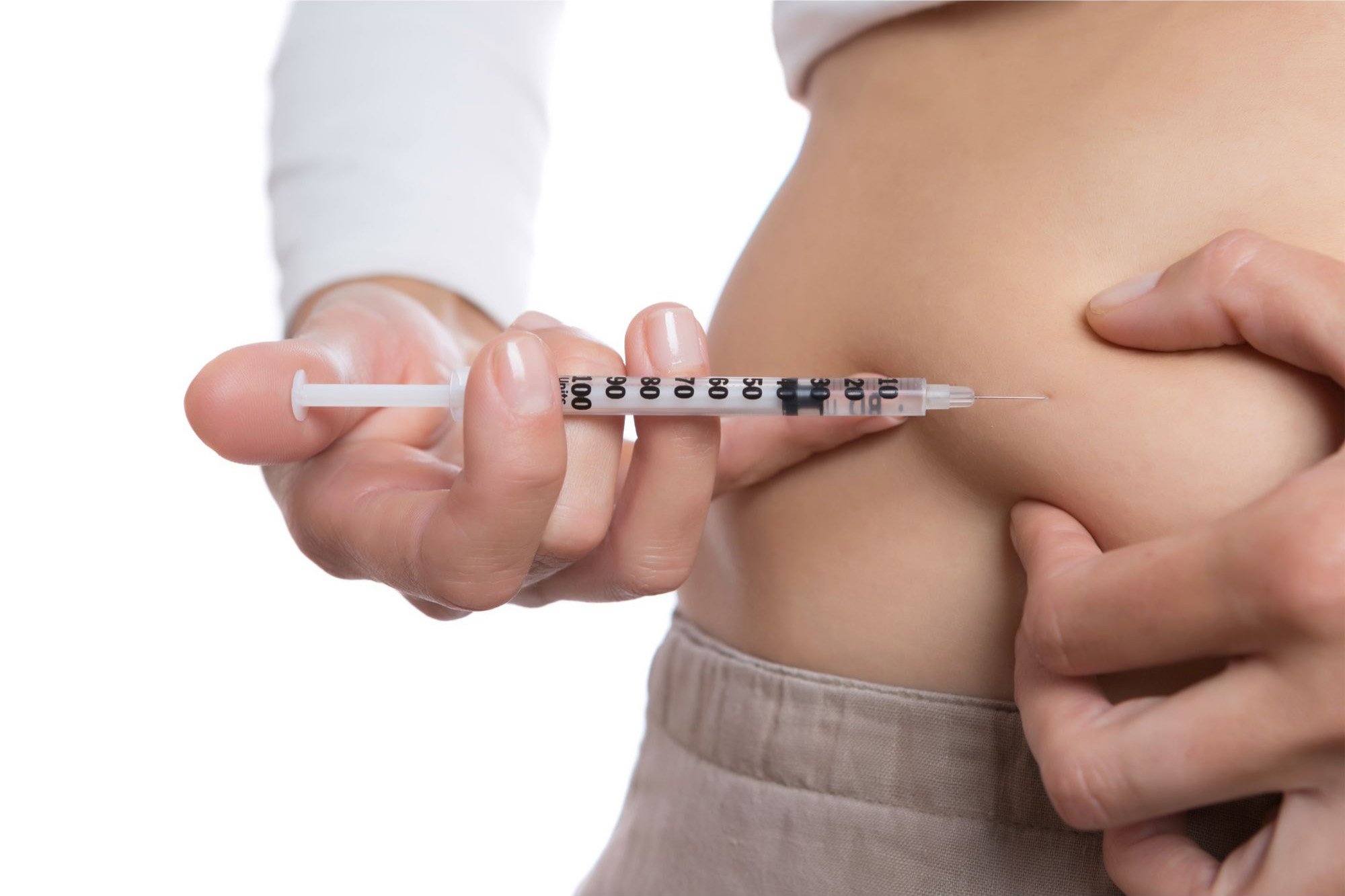
A startling health trend is emerging among type 2 diabetes patients, with nearly 40% of newly diagnosed individuals abandoning their crucial medication within just 12 months of diagnosis. Experts from UVA Health have shed light on this concerning pattern, warning that such medication discontinuation can significantly compromise patients' long-term health and management of the chronic condition.
The research highlights a critical challenge in diabetes care: patient adherence. By stopping their prescribed treatments prematurely, these individuals are putting themselves at substantial risk of developing serious health complications. Diabetes management requires consistent medication and lifestyle modifications, and breaking this regimen can lead to potentially devastating consequences.
Health professionals emphasize the importance of patient education and support in maintaining consistent treatment. Understanding the reasons behind medication discontinuation—whether they stem from side effects, cost concerns, or lack of immediate symptom relief—is crucial in developing strategies to improve patient compliance and overall health outcomes.
