Water Crisis Deepens: Prichard's Desperate Millions and the Federal Environmental Crossroads
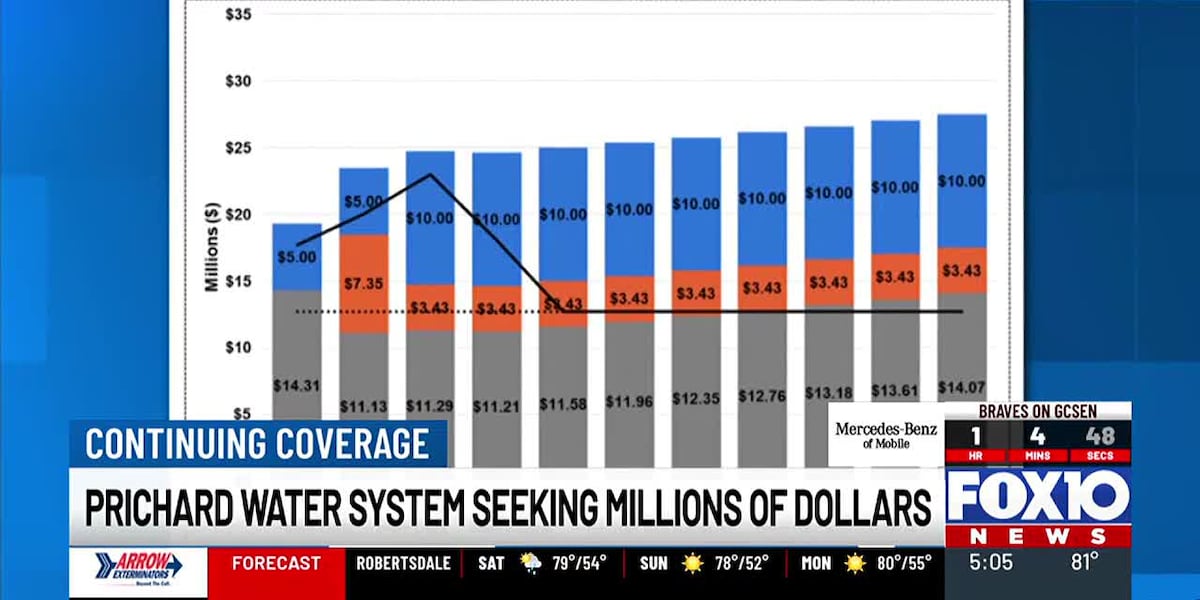
The water utility serving Prichard and Chickasaw is facing a critical financial challenge, desperately seeking substantial funding to address its ongoing infrastructure issues. John S. Young Jr., the court-appointed receiver managing the water system since 2023, has made significant progress by securing a $5.8 million grant from the Alabama Department of Environmental Management.
However, Young candidly admits that this financial injection is merely a drop in the ocean of needed repairs and improvements. The current political landscape presents formidable obstacles in sourcing additional funding, making the utility's path to financial stability increasingly complex.
Despite the challenges, Young remains committed to finding innovative solutions to revitalize the water system and ensure reliable service for the communities of Prichard and Chickasaw. The $5.8 million grant represents a crucial first step, but substantial work remains to fully rehabilitate the struggling utility infrastructure.
